ibidi细胞定位格子培养皿µ-Dish 35mm Grid-500
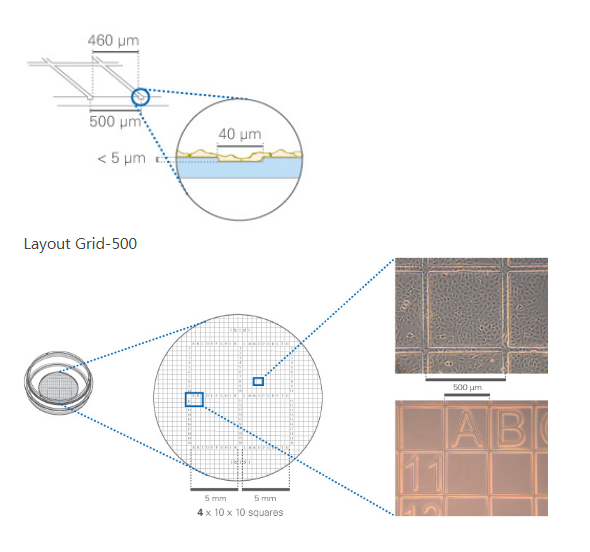
35mm具500um网格刻度 ibidi标准底部的培养皿

应用:
1.细胞或细胞簇的再定位
2.细胞计数,例如:细胞转染效率计算
3.细胞运动观察
4.细胞显微操作中单细胞处理
货号:
| 货号 | 产品名称 | 规格(个/盒) |
| 81148 | µ-Dish 35 mm,高壁,玻璃底,50微米格子培养皿 | 30 |
| 81168 | µ-Dish 35 mm,高壁,玻璃底,500微米格子培养皿 | 30 |
| 80156 | µ-Dish 35 mm,低壁,ibiTreat底部处理,500微米格子培养皿 | 60 |
| 80151 | µ-Dish 35 mm,低壁,无包被,500微米格子培养皿 | 60 |
| 81166 | µ-Dish 35 mm,高壁,ibiTreat底部处理,500微米格子培养皿 | 60 |
| 81161 | µ-Dish 35 mm,高壁,无包被,500微米格子培养皿 | 60 |
产品特点:
1.特别适合细胞或细胞簇的定位和重找回;
2.独特的ibidi标准底部设计,180um的盖玻片尺寸底部厚度,适合高分辨率显微观察;
3.独特的 ibiTreat 底部包被,适合大多数细胞的贴壁培养;
4.特殊盖部设计减小液体挥发。
技术特征:
1.直径为35mm标准样式的培养皿;
2.具500µm 网格刻度;
3.字母或数字标记(A-U; 1-20);
4.替代选择的玻璃底部产品:µ-Slide 35 mm, high glass bottom with Grid-50 or with Grid-500;
5.独特的 ibiTreat 组织培养处理表面适合大多数细胞的贴壁生长;
6.生物相容性材料制作,不含胶水,无细胞毒性影响;
7.特殊的盖部设计,减小液体挥发。
产品规格:
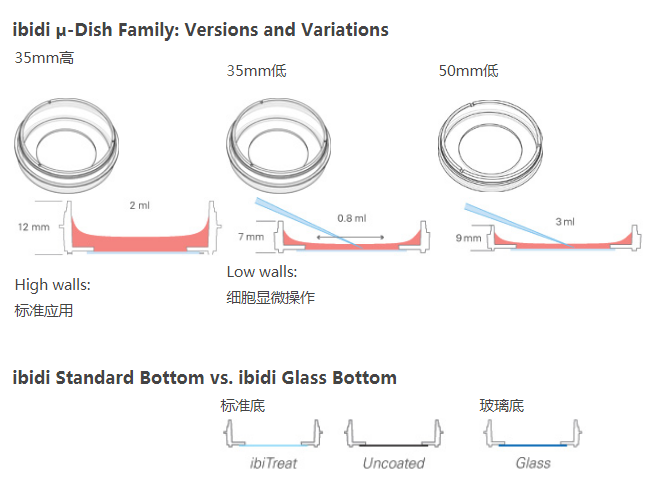
| Grid repeat distance | 500 µm | Growth area | 3.5 cm2 |
| Ø µ-Dish | 35 mm | Growth area | 21 mm |
| Volume high / low | 2 / 0.8 ml | Height with lid high / low | 14 / 9 mm |
| 底部 | Ibidi标准 | ||
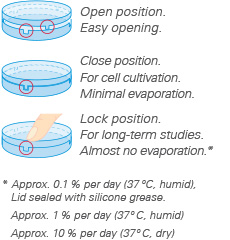
Lid with Lock Position
The special lock feature in all ibidi µ-Dishes enables the user to minimize evaporation. The lock position provides excellent conditions for long term studies in non humidified environments. Gas exchange (carbon dioxide, oxygen) during cell culture is maintained thanks to the gas permeable plastic material of the dish.
TIP: Use the locking feature only if minimal evaporation is
required, i.e., outside incubators, non humidified microscopy stages, etc.
| Optical properties | ||
| Refractive index (nD 589 nm) | 1.52 | 1.52 |
| Abbe number | 56 | 55 |
| Thickness | #1.5 (180 µm) | #1.5 (170 µm) |
| Material | Microscopy plastic | D 263M Schott borosilicate glass |
| Autofluorescence | Low | Low |
| Transmission | Very high (even ultraviolet) | High (ultraviolet restrictions) |
| Birefringence (DIC) | Low (DIC compatible*) | Low (DIC compatible*) |
| Other aspects | ||
| Surface modifications | ibiTreat – tissue culture treated Uncoated – hydrophobic |
Only pure glass |
| Protein coatings | Possible | Possible |
| Gas permeable | Yes | No |
| Material flexibility | High | Low |
| Breakable | No | Yes |
| Recommended for | All kinds of fluorescence microscopy | TIRF and single photon |
