前列腺素 E2 酶联免疫试剂盒
PGE2 ELISA kit
- 产品特性
- 相关资料
- Q&A
- 参考文献
![]() 前列腺素 E2 酶联免疫试剂盒
前列腺素 E2 酶联免疫试剂盒
PGE2 ELISA kit
用于炎症和类花生酸研究的高灵敏度前列腺素E2酶联免疫试剂盒。
研究背景:前列腺素 E2(PGE2)由于其在炎症、癌症、动脉粥样硬化、自身免疫性疾病和脓毒症中具有重要地位而被广泛研究。氧化的花生四烯酸通过前列腺素合成酶(COX-1和COX-2)生成前列腺素 H2(PGH2),被前列腺素合成酶进一步代谢成主要产物前列腺素 E2(PGE2)。前列腺素 E2(PGE2)通过与细胞表面的 G-蛋白偶联受体(EP1、EP2、EP3 和 EP4)的结合来介导自分泌和旁分泌的信号传导,从而调节磷脂酶C和腺苷酸环化酶活性。PGE2 作为一种治疗靶点,无论是通过 COX 抑制剂(NSAIDS)调节其合成,还是通过下调其与受体结合或结合拮抗剂,都引起了人们极大的兴趣。在各种组织中产生的前列腺素 E2(PGE2)已在多种生理过程中表现出了调节作用,包括在肾脏中尿钠排泄,血管中平滑肌的弹性,以及单核细胞和巨噬细胞对损伤组织的炎症作用。
◆产品特点
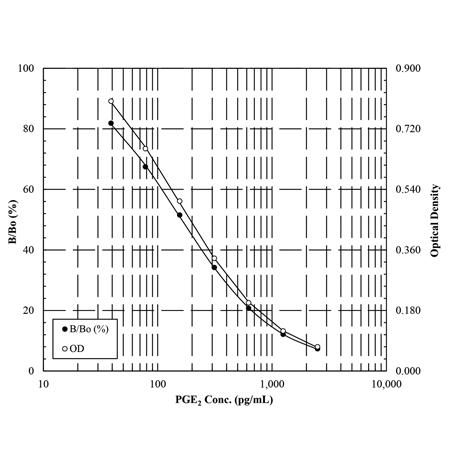
● 高灵敏度测定,可检测最少 13.4 pg/mL 的前列腺素 E2
● 3小时内即可获得多达37个样本重复检测的高通量格式的结果
● 广泛引用于同行评审文献中
● 准备使用的液体颜色编码试剂以便减少错误发生
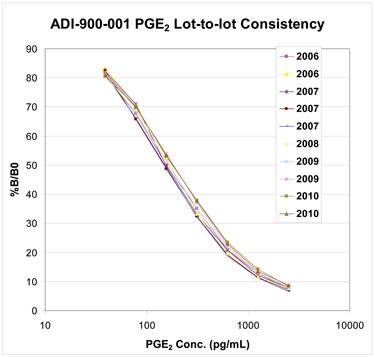
● 每次使用和不同批次产品获得良好重复性的结果
 |
 |
|
[1] |
Colon cancer-derived myofibroblasts increase endothelial cell migration by glucocorticoid-sensitive secretion of a pro-migratory factor: Z. Drebert, et al.; Vascul. Pharmacol. 89, 19 (2017), Application(s): Determine the concentrations of prostanoids in conditioned medium from myofibroblasts and HUVECs, and in HUVEC lysates, Abstract; |
|
[2] |
Expression of toll-like receptor-1 by bradykinin in human gingival fibroblasts: J.A. Arreguin-Cano T; Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 10, 1283 (2017), Application(s): Measurement of PGE2 in supernatant., Full Text |
|
[3] |
Human and feline adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells have comparable phenotype, immunomodulatory functions, and transcriptome: H.C. Clark, et al.; Stem Cell Res. Ther. 8, 69 (2017), Application(s): Measurement of PGE2 in supernatant of human and feline cells., Abstract; Full Text |
|
[4] |
Novel augmentation by bufalin of protein kinase C-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and IL-8 production in human breast cancer cells: H.T. Chen, et al.; Innate Immun. 23, 54 (2017), Abstract; Full Text |
|
[5] |
Prostaglandin E2 stimulates the expression of cumulus expansion-related genes in pigs: the role of protein kinase B: M. Blaha, et al.; Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 130, 38 (2017), Application(s): ELISA using pig samples, Abstract; |
|
[6] |
A positive feedback loop between progesterone and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1-mediated PGE2 promotes production of both in mouse granulosa cells: K. Tamura, et al.; Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 123, 56 (2016), Application(s): Measurement of PGE2 in the culture media, Abstract; |
|
[7] |
Anti-inflammatory effects of 6′-O-acetyl mangiferin from Iris rossii Baker via NF-κb signal blocking in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells: J.H. Jang, et al.; Chem. Biol. Interact. 2797, 30303 (2016), Application(s): Determination of PGE2 production, Abstract; |
|
[8] |
Dimethyl fumarate activates the prostaglandin EP2 receptor and stimulates cAMP signaling in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: S.E. Fiedler, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 475, 19 (2016), Application(s): Supernatant PGE2 was measured, Abstract; |
|
[9] |
Directly interact with Keap1 and LPS is involved in the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of (-)-epicatechin-3-gallate in LPS-induced macrophages and endotoxemia: Y.S. Chiou, et al.; Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 94, 1 (2016), Application(s): Measurement of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) level in culture medium, Abstract; |
|
[10] |
Effects of Almond- and Olive Oil-Based Docosahexaenoic- and Vitamin E-Enriched Beverage Dietary Supplementation on Inflammation Associated to Exercise and Age: X. Capo, et al.; Nutrients 8, 619 (2016), Application(s): Cytokine, Eicosanoids and Adhesion Molecules Determination, plasma, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[11] |
Enhanced anti-inflammatory activity of brown seaweed Laminaria japonica by fermentation using Bacillus subtilis: H.T.V. Lin, et al.; Process Biochem. (2016), Application(s): Measurement of prostaglandin E2 (PAGE2), cell supernatant, |
|
[12] |
Grid-like surface structures in thermoplastic polyurethane induce anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic processes in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Y. Roger, et al.; Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 148, 104 (2016), Application(s): ELISA using human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell supernatant, Abstract; |
|
[13] |
Implantation and pregnancy outcome of Sprague-Dawley rats fed with low and high salt diet: G.O. Oludare, et al.; Middle East Fertil. Soc. J. (2016), Application(s): Measured rat serum PGE2 levels, |
|
[14] |
In vitro bioactive properties of phlorotannins recovered from hydrothermal treatment of Sargassum muticum: M.P. Casas, et al.; Sep. Purif. Technol. 167, 117 (2016), Application(s): Determination of the amount of PGE2 in thawed plasma supernatants, |
|
[15] |
Isolation and Identification of a Flavone Apigenin from Marine Red Alga Acanthophora spicifera with Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Activities: G.A. El Shoubaky, et al.; J. Exp. Neurosci. 10, 21 (2016), Application(s): TNF-α measured in mouse blood samples, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[16] |
Local intra-uterine Ang-(1-7) infusion attenuates PGE2 and 6-keto PGF1α in decidualized uterus of pseudopregnant rats: K.B. Brosnihan, et al.; Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 14, 68 (2016), Application(s): Assaying tissue extracts, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[17] |
MRI-Based Assessment of Intralesional Delivery of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Model of Equine Tendonitis: A. Scharf, et al.; Stem Cells Int. 2016, 1 (2016), Application(s): Assessing the ability of MSCs to modulate the inflammatory response, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[18] |
Resokaempferol-mediated anti-inflammatory effects on activated macrophages via the inhibition of JAK2/STAT3, NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways: Q. Yu, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 38, 104 (2016), Application(s): PGE2 was measured in mouse supernatant, Abstract; |
|
[19] |
The Prostaglandin E2-EP3 Receptor Axis Regulates Anaplasma phagocytophilum-Mediated NLRC4 Inflammasome Activation: X. Wang, et al.; PLoS One 12, e1005803 (2016), Application(s): PGE2 measurement in cell lysates, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[20] |
Antagonizing Effects of Aspartic Acid against Ultraviolet A-Induced Downregulation of the Stemness of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: K. Jung, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0124417 (2015), Application(s): ELISA using human culture supernatant , Abstract; Full Text |
|
[21] |
Anti-inflammatory effect of desoxo-narchinol-A isolated from Nardostachys jatamansi against lipopolysaccharide: J.Y. Shin, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 29, 730 (2015), Application(s): PGE2 level was measured by ELISA in mice, Abstract; |
|
[22] |
Effectiveness of the combinational treatment of Laminaria japonica and Cistanche tubulosa extracts in hair growth: K. Shin, et al.; Lab. Anim. Res. 31, 24 (2015), Application(s): ELISA using mouse exudate, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[23] |
Insight into the molecular mechanism of an herbal injection by integrating network pharmacology and in vitro: Y.M. Ma, et al.; J. Ethnopharmacol. 173, 91 (2015), Application(s): ELISA using mouse RAW264.7 cells , Abstract; |
|
[24] |
Lipin-1 contributes to modified low-density lipoprotein-elicited macrophage pro-inflammatory responses: A.R. Navratil, et al. ; Atherosclerosis 242, 424 (2015), Application(s): ELISA using mouse cell culture supernatant, Abstract; |
|
[25] |
Molecular characterization and knock-down of salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) prostaglandin E synthase: C. Eichner, et al.; Exp. Parasitol. 159, 79 (2015), Application(s): ELISA Kit measuring PGE2 levels in salmon lice, Abstract; |
|
[26] |
Prostaglandin E2 Production and T Cell Function in Mouse Adenovirus Type 1 Infection following Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation: M.K. McCarthy, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0139235 (2015), Application(s): PGE2 concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid , Abstract; Full Text |
|
[27] |
Role of gastric acid inhibition, prostaglandins and endogenous-free thiol groups on the gastroprotective effect of a proteolytic fraction from Vasconcellea cundinamarcensis latex: A. Silva, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 67, 133 (2015), Application(s): EIA using rat tissue samples, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[28] |
Supplement of 5-hydroxytryptophan before induction suppresses inflammation and collagen-induced arthritis: T.H. Yang, et al. ; Arthritis. Res. Ther. 17, 364 (2015), Application(s): Measurement of PGE2 in mice serum samples, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[29] |
The cancer pain related factors affected by celecoxib together with cetuximab in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Y. Yang, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 70, 181 (2015), Application(s): ELISA using human culture medium, Abstract; |
|
[30] |
The Receptor CMRF35-Like Molecule-1 (CLM-1) Enhances the Production of LPS-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Mediators during Microglial Activation: A. Ejarque-Ortiz, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0123928 (2015), Application(s): ELISA using mouse microglial supernatant, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[31] |
Inhibition of COX-2 and PGE2 in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by lonimacranthoide VI, a chlorogenic acid ester saponin: F. Guan, et al.; Biomed. Rep. 2, 760 (2014), Application(s): Assay of LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[32] |
Possible roles of COX-1 in learning and memory impairment induced by traumatic brain injury in mice: J. Shang, et al.; Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 47, 1050 (2014), Application(s): Analysis of PGE2 levels in mouse hippocampus tissue, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[33] |
Prostaglandin E2 promotes features of replicative senescence in chronically activated human CD8+ T cells: J.P. Chou, et al.; PLoS One 9, e99432 (2014), Application(s): EIA using cell culture supernatants, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[34] |
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidative and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitory properties of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rh2 in cultured macrophages and keratinocytes: W.Y. Choi, et al.; J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 65, 310 (2013), Application(s): EIA using culture supernatants, Abstract; |
|
[35] |
Colorectal carcinoma-derived fibroblasts modulate natural killer cell phenotype and antitumor cytotoxicity: T. Li, et al.; Med. Oncol. 30, 663 (2013), Application(s): EIA using culture supernatants, Abstract; |
|
[36] |
Melanoma-educated CD14+ cells acquire a myeloid-derived suppressor cell phenotype through COX-2-dependent mechanisms: Y. Mao, et al.; Cancer Res. 73, 3877 (2013), Application(s): EIA using culture supernatants, Abstract; |
|
[37] |
Microenvironment generated during EGFR targeted killing of pancreatic tumor cells by ATC inhibits myeloid-derived suppressor cells through COX2 and PGE2 dependent pathway: A. Thakur, et al.; J. Transl. Med. 11, 35 (2013), Application(s): EIA using culture supernatants from 3D co-cultures, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[38] |
Prostaglandin E2 alteration in contraceptive consumers: as a risk factor for inflammatory diseases: M.S. Pour, et al.; Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 287, 1031 (2013), Application(s): EIA using human serum, Abstract; |
|
[39] |
Transmigration of Neural Stem Cells across the Blood Brain Barrier Induced by Glioma Cells: M. Díaz-Coránguez, et al.; PLoS One 8, e60655 (2013), Application(s): Quantification was done in 4 day CM derived from rat astrocytes and glioma C6 cells using ELISA, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[40] |
XH-14, a novel danshen methoxybenzo[b]furan derivative, exhibits anti-inflammatory properties in lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW 264.7 cells: G.M. Park, et al.; J. Inflamm. 10, 1 (2013), Application(s): EIA using culture supernatants, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[41] |
Acacetin protects dopaminergic cells against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine-induced neuroinflammation in vitro and in vivo: H.G. Kim, et al.; Biol. Pharm. Bull. 35, 1287 (2012), Application(s): EIA using culture supernatants, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[42] |
Hepatocellular carcinoma-associated fibroblasts trigger NK cell dysfunction via PGE2 and IDO: T. Li, et al.; Cancer Lett. 318, 154 (2012), Application(s): EIA using culture supernatants, Abstract; |
|
[43] |
Lycorine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 up-regulation in RAW264.7 cells through suppressing P38 and STATs activation and increases the survival rate of mice after LPS challenge: J. Kang, et al.; Int. Immunopharmacol. 12, 249 (2012), Application(s): EIA using culture supernatants, Abstract; |
|
[44] |
Matrix metalloproteinase-19 is a key regulator of lung fibrosis in mice and humans: G. Yu, et al.; Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 186, 752 (2012), Application(s): PGE2 from mice BAL was measured, Abstract; |
|
[45] |
Delta6-desaturase (FADS2) deficiency unveils the role of omega3- and omega6-polyunsaturated fatty acids: W. Stoffel, et al.; EMBO J. 27, 2281 (2008), Application(s): EIA using tissue, Abstract; |
|
[46] |
Anti-inflammatory effects of isoflavone powder produced from soybean cake: T.H. Kao, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 55, 11068 (2007), Application(s): EIA using peritoneal exudate fluid and peritoneal exudate cell supernatant, Abstract; |
|
[47] |
Celecoxib inhibits Cdx2 expression and prevents gastric cancer in Helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils: S. Futagami, et al.; Digestion 74, 187 (2006), Abstract; |
|
[48] |
Spinal inflammatory hyperalgesia is mediated by prostaglandin E receptors of the EP2 subtype: H. Reinold, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 115, 673 (2005), Application(s): PGE2 from the thoracolumbar segment of the spinal cord was measured, mice, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[49] |
Effect of a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, nimesulide, on the growth of lung tumors and their expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and peroxisome proliferator- activated receptor-gamma: M.S. Shaik, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 1521 (2004), Application(s): EIA using mouse tissue, Abstract; |
|
[50] |
Nonopioid actions of intrathecal dynorphin evoke spinal excitatory amino acid and prostaglandin E2 release mediated by cyclooxygenase-1 and -2: L. Koetzner, et al.; J. Neurosci. 24, 1451 (2004), Application(s): EIA using dialysate, Abstract; |
|
[51] |
Differential expression of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase in macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells: S. Al-Darmaki, et al.; J. Immunol. 170, 167 (2003), Application(s): EIA using human culture supernatants, Abstract; |
|
[52] |
Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by rofecoxib attenuates the growth and metastatic potential of colorectal carcinoma in mice: M. Yao, et al.; Cancer Res. 63, 586 (2003), Application(s): Concentration of PGE2 in splenic tumor cystosolic fractions were determined using mouse tissue, Abstract; |
|
[53] |
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 is a major terminal synthase that is selectively up-regulated during cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin E2 production in the rat adjuvant-induced arthritis model: D. Claveau, et al.; J. Immunol. 170, 4738 (2003), Application(s): PGE2 production was determined by enzyme immunoassay analysis using rat tissue, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[54] |
Increased levels of the pro-inflammatory prostaglandin PGE2 in CSF from ALS patients: G. Almer, et al.; Neurology 58, 1277 (2002), Application(s): EIA using cerebral spinal fluid, Abstract; |
|
[55] |
The effects of periodontal therapy on intracrevicular prostaglandin E2 concentrations and clinical parameters in pregnancy: F. Yalcin, et al.; J. Periodontol. 73, 173 (2002), Application(s): EIA using gingival crevicular fluid, Abstract; |
|
[56] |
Promoter methylation regulates Helicobacter pylori-stimulated cyclooxygenase-2 expression in gastric epithelial cells: M. Akhtar, et al.; Cancer Res. 61, 2399 (2001), Application(s): EIA using cell culture supernatant, Abstract; Full Text |
|
[57] |
Inflammatory agonists induce cyclooxygenase type 2 expression by human neutrophils: C.G. Maloney, et al.; J. Immunol. 160, 1402 (1998), Application(s): EIA using human cell culture supernatant, Abstract; |
|
[58] |
Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition by nimesulide in man: L. Cullen, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 287, 578 (1998), Application(s): EIA using plasma, Abstract; |
| 产品编号 | 产品名称 | 产品规格 | 产品等级 | 备注 |
| ADI-900-001 | PGE2 ELISA kit 前列腺素E2酶联免疫试剂盒 |
96 wells | – | – |
| ADI-901-001 | PGE2 ELISA kit 前列腺素E2酶联免疫吸附试剂盒 |
5×96 wells | – | – |
| ENZ-KIT179-0200 | PLAQPRO™ Lp-PLA2 Assay PLAQPRO™ Lp-PLA2 化验 |
200 tests | – | – |
| ADI-930-001 | PGE2 high sensitivity ELISA kit PGE2高灵敏度酶联免疫试剂盒 |
96 wells | – | – |
| ADI-931-001 | PGE2 high sensitivity ELISA kit 前列腺素E2 高灵敏度 ELISA kit |
5×96 wells | – | – |
| ADI-900-068 | LTB4 ELISA kit 白三烯B4 酶联免疫试剂盒 |
96 wells | – | – |
| ADI-901-068 | LTB4 ELISA kit 白三烯B4 酶联免疫试剂盒 |
5×96 wells | – | – |
| ADI-900-092 | 11-dehydro-TXB2 ELISA kit 11-脱氢-血栓烷素B2 ELISA试剂盒 |
96 wells | – | – |
| 免责声明 |
|
1. 本公司密切关注本网站发布的内容,但不保证发布内容的准确性、完整性、可靠性和最新性等。 2. 本公司不保证使用本网站期间不会出现故障或计算机病毒污染的风险。 3. 无论何种原因,使用本网站时给用户或第三方造成的任何不利或损害,本公司概不负责。此外,对于用户与其他用户或第三方之间因本网站发生的任何交易、通讯 3. 或纠纷,本公司概不负责。 4. 本网站可提供的所有产品和服务均不得用于人体或动物的临床诊断或治疗,仅可用于科研等非医疗目的。如任何用户将本网站提供的产品和服务用于临床诊断或治 4. 疗,以及其他特定的用途或行为,本公司概不保证其安全性和有效性,并且不负任何相关的法律责任。 |
