Ionic Liquid Screen-Hampton离子液体删选试剂
上海金畔生物代理Hampton research品牌蛋白结晶试剂耗材工具等,我们将竭诚为您服务,欢迎访问Hampton research官网或者咨询我们获取更多相关Hampton research品牌产品信息。


Products > Optimization Screens > Ionic Liquid Screen > Ionic Liquid Screen
Ionic Liquid Screen
Applications
- Manipulate sample-sample & sample-solvent interactions to improve crystals or alter sample solubility
- Additive screen for protein crystallization
Features
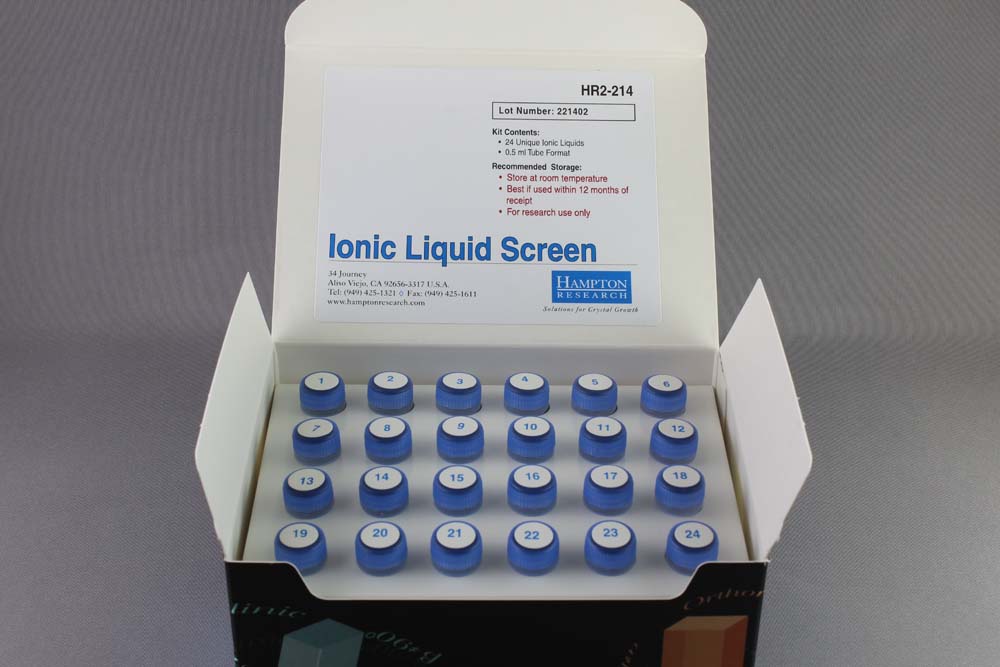
- 24 unique ionic liquids
- 0.5 ml tube format
Description
Ionic Liquid Screen is a kit designed to allow the rapid and convenient evaluation of 24 unique ionic liquids and their ability to influence the crystallization of the sample. The screen is designed to be compatible with most crystallization reagents including all reagents utilized in all of the Hampton Research screens.
Ionic liquids have been found effective as additives in protein crystallization, with different ionic liquids used to increase crystallization rates and crystal size.1-4 The inclusion of ionic liquids in crystallization experiments has been reported to lead to less crystal polymorphism as well as less precipitation at higher precipitant concentrations.25 Ionic liquids have been used as additives to produce crystals in reagents that had previously not resulted in crystallization and results suggest ionic liquids may be applicable for the solubilization and crystallization of membrane proteins.2
Ionic liquids are organic salts with melting points below 100°Celsius. They are thermally stable, nonflammable and demonstrate very low vapor pressure. Ionic liquids are soluble in a variety of organic and inorganic reagents and can be highly water soluble. Ionic liquids can demonstrate a degree of localized structuring about each ion compared to materials composed of disassociated ions, setting them apart from salt solutions.5-6 Ionic liquids can participate in ionic, hydrophobic and hydrogen bond interactions. Ionic liquids are often chaotropic, composed of low symmetry ions with charge delocalization and weak intermolecular interactions.1 These organic salts generally consist of combinations of organic cations and either an organic or inorganic anion. Ionic liquids have been demonstrated to suppress protein aggregation and significantly increase protein folding yields.7-8 Ionic liquids have been reported to stabilize protein activity and structure.9-11 The inclusion of the ionic liquid 1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (included in this kit) improved the thermal stability and solubility of integral membrane proteins for membrane proteomics study.12
Some ionic liquids, such as ethylammonium nitrate have water-like characteristics, including the capacity for hydrogen bonding and the promotion of micelle formation by some surfactants.13 Many ionic liquids are also organics acids and have ionic character in addition to the hydrophobic behavior, which makes them unique and useful solvents in protein chemistry.
Variation of the anion and the cation as well as the utilization of both soft (formate and acetate) and hard anions (nitrate) in the Ionic Liquid Screen reagents provides an additional dimension for evaluating the effects on ionic liquids on the solubility and crystallization of proteins. The Ionic Liquid Screen contains a set of 24 water soluble ionic liquids that comprise different cation (imidazolium, phosphonium, ammonium) and anion (borate, halides, sulfates, acetates, sulfonates, nitrates) structures for a diverse ionic liquid additive screen for use in improving the crystallization behavior and X-ray diffraction resolution of proteins.
Each of the 24 ionic liquids are preformulated in deionized water and sterile filtered using a 0.2 micron filter. Ionic liquid Screen contains 24 unique reagents, 0.5 milliliter each.
操纵样品-样品和样品-溶剂相互作用以改善晶体或改变样品溶解度
蛋白质结晶的添加剂筛选
特征
24种独特的离子液体
0.5 ml 试管规格
描述
Ionic Liquid Screen 是一个套件,旨在快速方便地评估 24 种独特的离子液体及其影响样品结晶的能力。该屏幕旨在与大多数结晶试剂兼容,包括所有 Hampton Research 屏幕中使用的所有试剂。已发现离子液体可作为蛋白质结晶的有效添加剂,使用不同的离子液体可提高结晶速率和晶体尺寸。 1-4 据报道,在结晶实验中加入离子液体可导致较少的晶体多晶型和较少的沉淀在更高的沉淀剂浓度下。25 离子液体已被用作添加剂以在以前不会导致结晶的试剂中产生晶体,结果表明离子液体可能适用于膜蛋白的增溶和结晶。 2
离子液体是熔点低于 100°C 的有机盐。它们具有热稳定性、不可燃性和极低的蒸气压。离子液体可溶于多种有机和无机试剂,并可高度溶于水。与由离解离子组成的材料相比,离子液体可以展示每个离子一定程度的局部结构,使它们与盐溶液区分开来。5-6 离子液体可以参与离子、疏水和氢键相互作用。离子液体通常是离液的,由具有电荷离域和弱分子间相互作用的低对称离子组成。1 这些有机盐通常由有机阳离子和有机或无机阴离子的组合组成。离子液体已被证明可抑制蛋白质聚集并显着增加蛋白质折叠产率。7-8 据报道,离子液体可稳定蛋白质活性和结构。9-11 离子液体 1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium 四氟硼酸盐的加入(包含在该试剂盒中)提高了膜蛋白质组学研究中整合膜蛋白的热稳定性和溶解性。 12
一些离子液体,如硝酸乙基铵,具有类似水的特性,包括氢键的能力和一些表面活性剂促进胶束形成的能力。 13 许多离子液体也是有机酸,除了疏水行为外还具有离子特性,这使它们成为蛋白质化学中独特而有用的溶剂。
离子液体筛选试剂中阴离子和阳离子的变化以及软阴离子(甲酸根和乙酸根)和硬阴离子(硝酸根)的使用为评估离子液体对蛋白质溶解度和结晶的影响提供了额外的维度.离子液体筛网包含一组 24 种水溶性离子液体,包含不同的阳离子(咪唑鎓、鏻、铵)和阴离子(硼酸盐、卤化物、硫酸盐、醋酸盐、磺酸盐、硝酸盐)结构,用于多种离子液体添加剂筛网改善蛋白质的结晶行为和 X 射线衍射分辨率。
24 种离子液体中的每一种都在去离子水中预先配制,并使用 0.2 微米过滤器进行无菌过滤。离子液体 Screen 包含 24 种独特的试剂,每种试剂 0.5 毫升。
Ionic Liquid Screen


CAT NO
HR2-214
NAME
DESCRIPTION
0.5 ml, tube format
PRICE
$284.00
cart quote
Support Material(s)
 HR2-214 Ionic Liquid Screen Documents
HR2-214 Ionic Liquid Screen Documents HR2-214 Ionic Liquid SDS
HR2-214 Ionic Liquid SDS Ionic Liquid Screen Formulation and Scoring Data
Ionic Liquid Screen Formulation and Scoring DataRelated Item(S)
- Individual Ionic Liquid Reagents
References
1. Pusey, M.L., Paley, M.S., Turner, M.B., and Rogers, R.D. 2007. Protein crystallization using room temperature ionic liquids. Crystal Growth & Design. 74:787-793.
2. Hekmat, D., Hebel, D., Sebastian, J. Schmidt, M., and Weuster-Botz, D. 2007. Advanced protein crystallization using water-soluble ionic liquids as crystallization additives. Biotech. Lett., 29:703-1711.
3. Garlitz, J.A., Summers, C.A., Flowers, R.A. and Borgstahl, G.E.O. 1999. Ethylammonium nitrate: A protein crystallization reagent. Acta Cryst. D53:2037-2038.
4. Judge, R.A., Takahashi, S., Longnecker, K.L. Fry, E.H., Abad-Zapatero, C., and Chi, M.L. 2009. The effects of ionic liquids on protein crystallization and X-ray diffraction resolution. Crystal Growth & Design 9:3463-3469.
5. Bowran, D.T., Hardacre, C. Holbrey, J.D., McMath, J.E., and Soper, A.K. 2003. J. Chem. Phys. 118:173-178.
6. Cadena, C., Zhao, Q., Snurr, and R.Q., Maginn, E.J. 2006. J. Chem. Phys. B 110:2821-2832.
7. Summers, C.A. and Flowers, R.A. 2000. Protein renaturation by the liquid organic salt ethylammonium nitrate. Protein Science 9:2001-2008.
8. Lange, C., Patil, G., and Rudolph, R. 2005. Ionic liquids as refolding additives: N′-alkyl and N′-(w-hydroxyalkyl) N-methylimidazolium chloride. Protein Science 14:2693-2701.
9. Lozano, P. , de Diego, T. Guegan, J.P., Vaultier, M., and Ibora, J.L. 2001. Stabilization of a-chymotrypsin by ionic liquids in transesterification reactions. Biotehnol. Bioeng. 75:363-369.
10. Baker, S.N., McCleskey, T.M., Pandy, S., and Baker, G.A. 2004. Fluorescence study of protein thermostability in ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2004:940-941.
11. De Diego, T., Lozano, P., Gmouth, S. Vaultier, M., and Iborra, J.L. 2004. Fluorescence and CD spectroscopic analysis of the a-chymotrypsin stabilization by the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methyimidazolium bis[(trifluormethyl)sulfonyl]amide. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 88:916-924.
12. Sun, L., Tao, D., Han, B., Ma, J., Zhu, G., Liang, Z., Shan, Y., Zhang, L., and Zhang, Y. 2010. Ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium tetrafluoroborate for shotgun membrane proteomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. DOI 10.1007/s0216-010-4381-5.
13. Evans, D.F., Yamauchi, A., Roman, R., and Casassa, E.Z. 1982. J. Colloids Interface Sci. 88:89-96.
14. Proteins in Ionic Liquids: Current Status of Experiments and Simulations. Christian Schrode, Top Curr Chem (J). 2017; 375(2): 25.
15. Ionic Liquids as Stabilization and Refolding Additives and Solvents for Proteins. Fujita K. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2018 Jul 13. doi: 10.1007/10_2018_65.
16. Fujita K. (2018) Ionic Liquids as Stabilization and Refolding Additives and Solvents for Proteins. In: . Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
